Cuban Currency Crisis: Informal Exchange Rates Surge, Impacting Daily Life
April 26, 2025
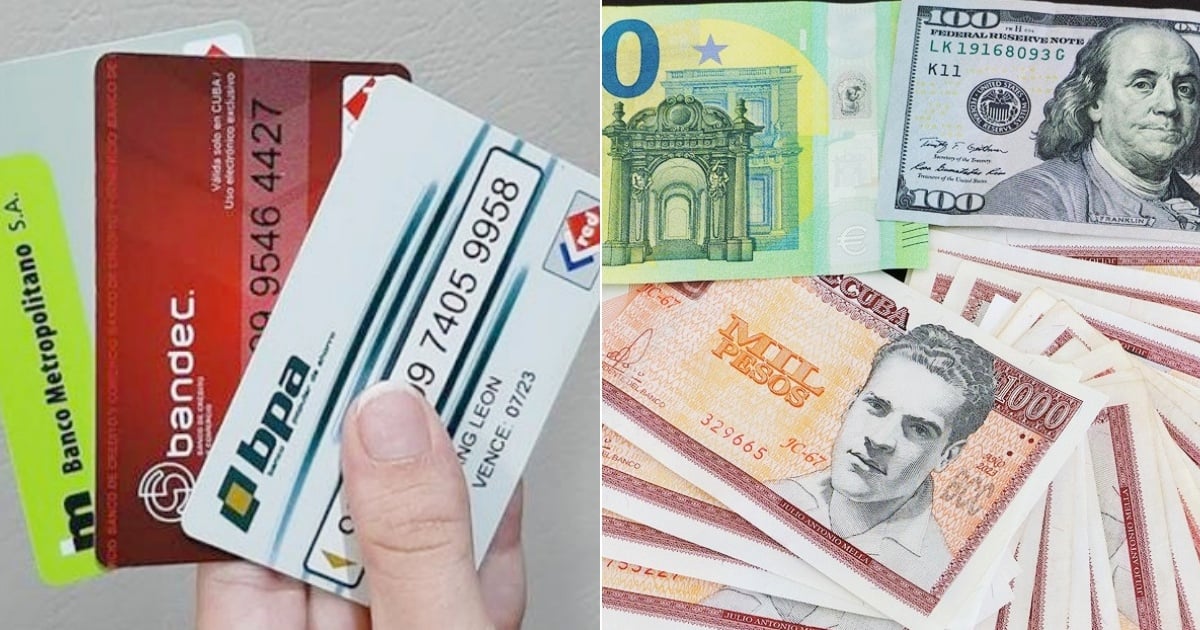
The Cuban economy continues to grapple with a volatile currency market, leaving citizens scrambling to protect their purchasing power. The informal exchange rates for the U.S.dollar, the euro, and the freely convertible currency (MLC) are under constant watch, reflecting the scarcity and inflation plaguing the island nation.
As of April 24,the MLC,a virtual currency used in Cuba to purchase goods in specific stores,experienced an increase. “the MLC scale again at 265 CUP,” climbing four pesos “in relation to the preceding day.”
While the MLC saw a slight rise, the U.S. dollar held steady. “In the case of the dollar, the US currency does not record changes and remains appraised in 365 CUP,” a rate that has been in place “since last Saturday.” The euro also remained stable. “The Euro, simultaneously occurring, remains stable in 380 CUP,” a level reached on April 23.
Fluctuating Fortunes: A Look at Currency Trends
The informal currency market in Cuba is notoriously dynamic, influenced by factors ranging from government policies to the availability of hard currency. Recent data indicates a potential shift in these trends.
“The median values of the three reference currencies in the last 24 hours marks an increase in the average sale of the dollar, a rise that could be consolidated, or not, in the next few hours.” This potential dollar valuation could further strain the Cuban economy, as many rely on dollars for essential goods and services.
Last week, a forecast suggested possible shifts in currency values during the remainder of April. the forecast indicated that an “valuation of the dollar and the euro is expected between 2.5 % and 4.8 %, while The MLC could fall to levels of 262 – 255 Cup per 1 mlc.” The forecast “estimated that the dollar is between 364 and 372 CUP, and the euro between 370 and 377 CUP.”
impact on Daily Life: Scarcity and Inflation
for ordinary Cubans, these fluctuating exchange rates have a direct and profound impact on their daily lives. “Cubans live pending the informal exchange rate of the dollar, the euro and the MLC because it determines its real purchasing power in a economy marked by scarcity and inflation.”
The devaluation of the Cuban peso (CUP) against foreign currencies means that imported goods, which are often essential, become more expensive. This can lead to shortages and further inflation, creating a vicious cycle for consumers.
“The volatility of change rates in cuba makes many citizens residing on the island closely follow the evolution of the informal market, in search of strategies to protect its purchasing power against the devaluation of the national currency.” Some Cubans are turning to option strategies, such as bartering or investing in durable goods, to preserve their wealth.
| Currency | Exchange Rate (CUP) |
|---|---|
| USD | 365 |
| EUR | 380 |
| MLC | 265 |
U.S. Policy and the Cuban Economy
U.S.policy toward Cuba continues to play a notable role in the island’s economic challenges. The decades-long embargo restricts trade and investment, limiting Cuba’s access to international markets. While some argue that the embargo is necessary to pressure the cuban government to improve its human rights record, others contend that it primarily hurts the Cuban people.
Remittances from the United States are a crucial source of income for many Cuban families. However, restrictions on sending money to Cuba through official channels have pushed more transactions into the informal market, contributing to the volatility of exchange rates.
The Counterargument: Stability Through Government Control
Some argue that increased government control over the Cuban economy and currency exchange is the solution to the current crisis. Proponents of this view suggest that stricter regulations and centralized management could stabilize exchange rates and curb inflation.
However, critics argue that such measures would likely stifle economic activity and further restrict individual freedoms. They point to the failures of past government interventions in the Cuban economy, arguing that a more market-oriented approach is needed to foster enduring growth.
FAQ: Navigating the Cuban Currency Market
How is the dollar exchange rate in the Cuban informal market?
The exchange rate of the US dollar in the Cuban informal market remains at 365 CUP. This stability has been observed since last Saturday, and a possible valuation of the dollar is expected in the coming weeks.
How much is the euro in the informal market of Cuba?
The euro is currently quoted at 380 CUP in the Cuban informal market. He has shown an upward trend in recent days, and is expected to continue increasing its value, according to forecasts of the Cuba and Finance Observatory of Cuba.
What is freely convertible currency (MLC) and what is its current value in cuba?
The freely convertible currency (MLC) is a virtual currency used in Cuba to buy products in specific stores.
Its current value in the informal market is 265 CUP. Despite recent ups and downs, the MLC has shown some volatility, and there is the expectation of a possible fall in its short term value.
Why is the informal exchange rate in Cuba vital?
The informal exchange rate is crucial in Cuba as it determines the real purchasing power of citizens. in a context of shortage and inflation, many Cubans depend on foreign currencies to acquire essential goods and protect their savings, as salaries in Cuban pesos are insufficient to meet basic needs.
what strategies do you think could effectively ease the economic burden on the Cuban people, considering all the constraints we’ve discussed? Share your thoughts in the comments below
Cuban Currency Crisis Interview: Expert Analysis on Informal Exchange rates
April 27, 2025
Archyde News Editor: Welcome to Archyde. Today, we’re discussing the ongoing currency crisis in Cuba. Joining us is Dr.Elena Rodriguez, a leading economist specializing in Latin American economies.Dr. Rodriguez, thank you for being here.
Dr. Elena Rodriguez: Thank you for having me. It’s a crucial topic with significant implications for Cubans.
Understanding the Current currency Landscape in Cuba
Archyde News Editor: Let’s start with the basics. The article highlights fluctuating informal exchange rates.Could you explain what’s currently happening with the currencies – the USD, EUR, adn MLC – and what’s driving these trends?
Dr. elena Rodriguez: Certainly. As of April 24th, we see the informal market rates as: 365 CUP for one USD, 380 CUP for one EUR, and 265 CUP for one MLC. The MLC, or freely convertible currency, has seen a recent uptick, while the dollar and euro have remained relatively stable, although this is temporary. The main drivers are scarcity, inflation, and government policy. The lack of access to hard currency fuels the informal market, where Cubans seek to protect their purchasing power.
The Impact on Daily Life
Archyde News Editor: The article emphasizes the impact on ordinary Cubans. How are these fluctuations affecting their daily lives and purchasing power?
Dr. Elena Rodriguez: It’s a constant struggle. The devaluation of the Cuban Peso (CUP) against the dollar and euro means that imported goods become more expensive. Since many essential goods are imported,this leads to inflation and shortages. The average monthly salary of around 4,000 CUP – equating to just over $10 USD at these exchange rates – highlights the economic hardship. Cubans are constantly monitoring the informal market to strategize their spending and savings.
Remittances and U.S. policy
Archyde News Editor: Remittances from the U.S. play a vital role. How do restrictions on sending money to Cuba through official channels contribute to the volatility of the informal market?
Dr. elena Rodriguez: Restrictions force more remittances through the informal market, increasing demand for these currencies within Cuba and further inflating the informal exchange rates. This is a significant headwind for families dependent on these funds. The U.S. embargo and resulting limitations on trade and investment amplify these issues, restricting Cuba’s access to foreign currency reserves.
Potential Solutions and Challenges
Archyde news Editor: Ther’s mention of different viewpoints regarding solutions government control versus a market-oriented approach. What are the potential benefits and drawbacks of each?
Dr. Elena Rodriguez: Increased government control, such as stricter exchange rate regulations, could theoretically stabilize rates in the short term. However, this often leads to reduced economic activity and limits individual freedoms, stifling entrepreneurship and innovation. A more market-oriented approach, while potentially leading to initial instability, can foster sustainable growth. It would require significant structural reforms, including allowing free market exchange rates and opening the economy to foreign investment, facing political hurdles with their own complexities.
Looking Ahead
Archyde News Editor: What are your predictions for currency trends in the coming weeks and months? Are there any signs of the crisis abating?
Dr. Elena Rodriguez: Based on current data and forecasts, we anticipate possible fluctuations particularly with dollar valuation. the MLC rate may also show some variance. Without significant policy changes, I do not see the immediate crisis abating. The Cuban economy’s dependence on imports, combined with the limited access to foreign currency, will maintain pressure on the CUP and the informal market. Any long-term solution requires wider economic reforms,and the advancement involves policy shifts from both within Cuba and U.S. relations.
A Question for Our Readers
Archyde News Editor: Dr. Rodriguez, thank you for your insights. Now for a question to our readers: What strategies do you think could effectively ease the economic burden on the Cuban people, considering all the constraints we’ve discussed? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
Dr. Elena Rodriguez: It’s my pleasure.