Hubble Captures Stunning Star Formation Details in Spiral Galaxy NGC 4941
by Archyde News Team | Published April 7, 2025
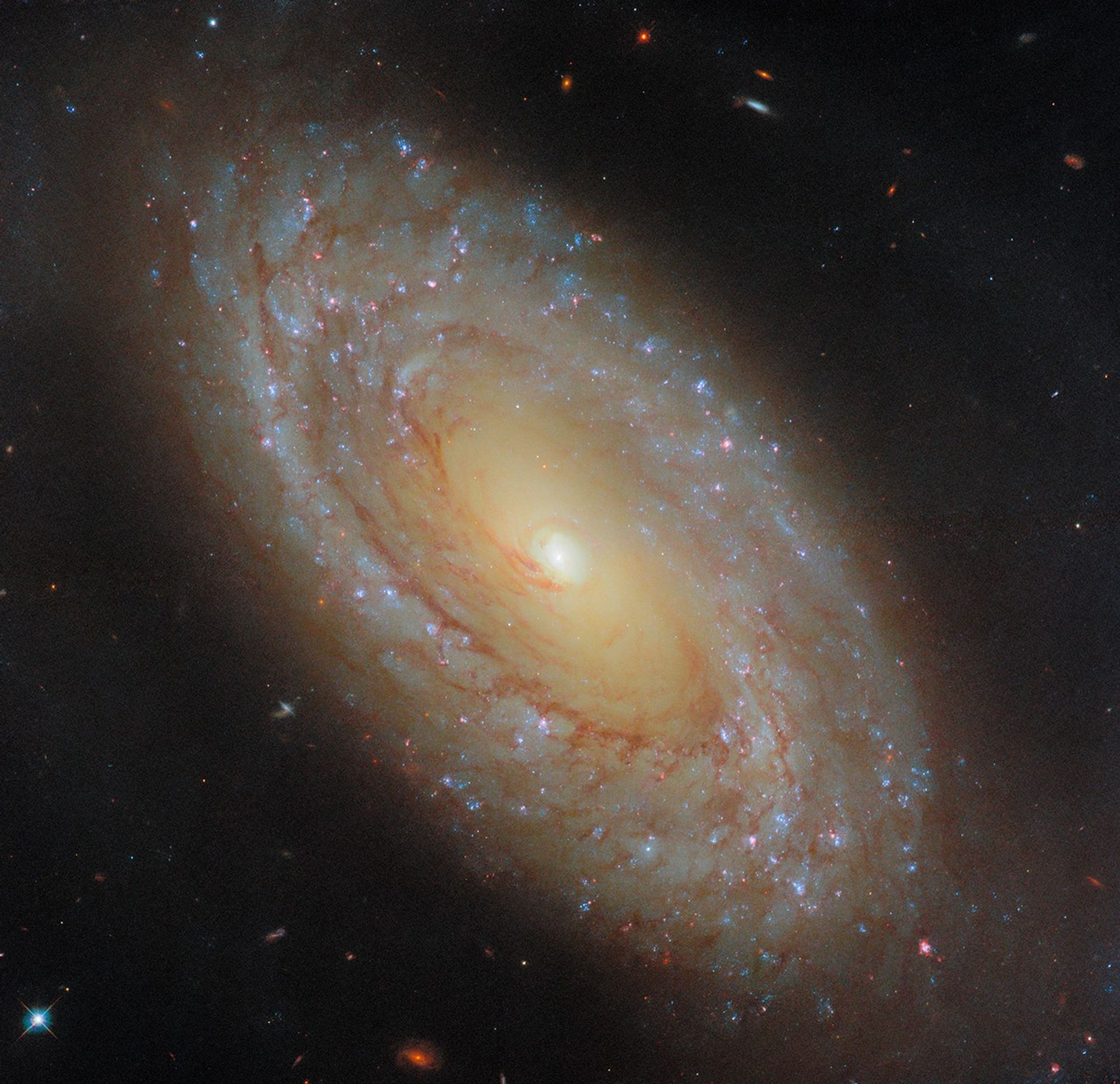
New images from the Hubble Space Telescope reveal unprecedented details of star birth and galactic evolution within the spiral galaxy NGC 4941.Located 67 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo, this galaxy offers a unique window into the complex interplay between star formation and the influence of an active galactic nucleus (AGN).
A Cosmic Neighbor Under Scrutiny
On april 4, 2025, the NASA Hubble Mission Team at Goddard Space Flight Center unveiled a breathtaking image of NGC 4941, a spiral galaxy relatively close to our own Milky Way. This proximity allows Hubble’s powerful instruments to resolve individual star clusters and the delicate structures of gas and dust that permeate the galaxy. The release of this image marks a critically important milestone in understanding the intricacies of star formation and how galaxies change over vast cosmic timescales.

For U.S. taxpayers, whose investments support missions like Hubble, this image isn’t just pretty; its a direct return on investment. The data collected helps train the next generation of American astronomers and engineers, fueling innovation in fields ranging from optics to data science.
Stellar Feedback: A Cosmic Balancing Act
The observations of NGC 4941 are part of an ongoing effort to understand “stellar feedback,” the process by which stars influence their surroundings. Consider it a cosmic version of cause and effect. As stars are born from dense clouds of gas, they emit powerful stellar winds and radiation. Massive stars eventually explode as supernovae, events that release tremendous amounts of energy into the surrounding space. These forces can disrupt the very clouds that spawned the stars, regulating the rate of future star formation.
Think of it like managing a community garden. If you plant too many seeds in one spot, they’ll compete for resources and none will thrive. Stellar feedback acts as a natural regulator, ensuring that star formation doesn’t spiral out of control.
By studying NGC 4941, scientists are gaining a deeper understanding of how this feedback mechanism operates, providing crucial insights into the evolution of galaxies. This research could have implications for understanding the formation of our own solar system and the conditions that led to the progress of life on Earth.
The Active Core: A Black Hole’s Influence
Adding another layer of complexity,NGC 4941 hosts an “active galactic nucleus (AGN)” at its heart. This AGN is powered by a supermassive black hole, an object with gravity so intense that nothing, not even light, can escape. As gas spirals toward the black hole, it heats up to millions of degrees, forming a superheated disk that emits radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. This radiation,along with powerful winds and jets of particles,exerts a significant influence on the galaxy’s environment.
Imagine a powerful spotlight shining from the center of a stadium. The AGN acts similarly, bathing the galaxy in intense energy that can affect star formation and the distribution of gas and dust.
A Dual Influence: Star Formation and Galactic Evolution
The combined effects of stellar feedback and the AGN shape not only the galaxy’s star formation rate but also its overall evolution. The interplay between these phenomena highlights the complex and dynamic nature of galaxies. hubble’s observations provide valuable data for astronomers to model and understand these intricate interactions. Understanding how both stars and active galactic nuclei influence their galactic environments is crucial for developing a thorough picture of galaxy evolution. Studying nearby galaxies like NGC 4941 allows researchers to examine these processes in detail, contributing to our broader understanding of the universe.
The NASA/ESA Hubble space Telescope has captured a stunning image of NGC 4941, a spiral galaxy located approximately 67 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. This relatively close proximity allows Hubble’s advanced instruments to resolve intricate details within the galaxy, including distinct star clusters and delicate filaments of gas and dust.
This dual influence presents a challenge for astronomers, but also an opportunity. By studying NGC 4941, researchers can disentangle the effects of star formation and AGN activity, gaining a more complete picture of how galaxies evolve over billions of years. This knowledge is crucial for understanding the history of the universe and our place within it.
Practical Applications and Future Research
While the study of distant galaxies might seem abstract, it has practical applications here on Earth. The technologies developed for space telescopes like Hubble, such as advanced sensors and data processing techniques, often find their way into other fields, including medicine, telecommunications, and materials science.
Furthermore, understanding the processes that govern star formation and galactic evolution can help us better understand the conditions necessary for the formation of planetary systems and the emergence of life. As we search for habitable planets beyond our solar system, insights from galaxies like NGC 4941 become increasingly valuable.
Future research will likely focus on combining Hubble’s observations with data from other telescopes,such as the James Webb Space Telescope,to obtain a more complete picture of NGC 4941.These multi-wavelength observations will allow astronomers to probe the galaxy’s structure and composition in greater detail, revealing new insights into the complex interplay between stars, gas, and the active galactic nucleus.
How is the active galactic nucleus, or AGN, impacting star formation in NGC 4941?
Archyde interviews Dr. Aris Thorne on Hubble’s NGC 4941 Galaxy Revelations
by Archyde News Team | Published April 8, 2025
Introduction: Unveiling cosmic Secrets
Archyde: Welcome, Dr. Thorne. Thank you for joining us. The recent Hubble image of the spiral galaxy NGC 4941 has captivated the scientific community and the public alike. For our readers,could you briefly paint a picture of what makes this galaxy so interesting?
Dr. Thorne: Thank you for having me. NGC 4941 is a fantastic subject. It’s relatively close, only 67 million light-years away, which allows Hubble to resolve astounding details. We’re seeing individual star clusters, the intricate structure of gas and dust, and the influence of an active galactic nucleus – it’s a cosmic laboratory ripe for study.
Delving into Star Formation and Stellar Feedback
Archyde: the article mentions “stellar feedback.” Could you elaborate on this process and its significance in the context of NGC 4941?
Dr. Thorne: Certainly. Stellar feedback describes how newly formed stars impact their surroundings. Massive stars emit powerful winds and radiation, and some eventually explode as supernovae. These events inject vast amounts of energy into the interstellar medium, possibly disrupting star formation and regulating future star birth. NGC 4941 offers a prime exmaple of this cosmic give-and-take.
Archyde: So, it’s a balancing act, ensuring star formation doesn’t happen too rapidly?
Dr. Thorne: Precisely. Think of it like a gardener pruning a plant to help it thrive. Stellar feedback is the galaxy’s way of managing resources, influencing its evolution over billions of years.
The Active Galactic Nucleus and Black Hole’s Influence
Archyde: NGC 4941 also has an active galactic nucleus, or AGN. What role does the supermassive black hole at its heart play?
Dr. Thorne: The AGN is powerful.It’s fueled by a supermassive black hole, devouring material that forms a superheated disk around it. This disk emits intense radiation and powerful winds. These combined effects significantly influence star formation and the distribution of gas and dust throughout the galaxy. The AGN acts like a cosmic spotlight, impacting the entire galactic habitat.
Combining Data for Extensive Understanding
Archyde: The article highlights the need to disentangle the effects of star formation and the AGN. How do astronomers achieve this?
dr. Thorne: It’s complex, but crucial. We compare observations of different wavelengths of light. Hubble provides incredible detail in the visible and ultraviolet, while othre telescopes, like the James Webb Space Telescope, offer insights in infrared. Analyzing data across multiple wavelengths helps us “see” the galaxy’s components separately,and then use them to build a more complete picture of galactic evolution.
Real-World Applications and Future Research
Archyde: Beyond the scientific merits, do these observations have any practical implications?
Dr. Thorne: Absolutely. The technology developed for space telescopes, like advanced sensors and data processing techniques, often finds applications in other fields, such as medicine or telecommunications. Furthermore, understanding star formation and galactic evolution provides insights into the conditions necessary for planets and possibly even life to develop.
Archyde: Fascinating! What’s the next step for studies on NGC 4941?
dr. Thorne: We will combine the data from Hubble with other telescopes’ data. Multi-wavelength observations will provide higher resolution imaging. Researchers will be able to model and understand the complex interactions happening in the galaxy more clearly.
Concluding thoughts and Reader Engagement
Archyde: Dr. Thorne, this has been enlightening.for our readers, if you could distill the most exciting aspect of this research, what would it be?
Dr. Thorne: I think it’s the chance to understand how galaxies grow up, and the complex interplay between stars and supermassive black holes in their nuclei. NGC 4941 is a great example of this. The ability to actually see these processes at work and model them is truly inspiring. What are your thoughts on how the AGN is impacting the stars in NGC 4941?