Hubble Space Telescope Marks 35th Anniversary with Breathtaking New Views
Table of Contents
- 1. Hubble Space Telescope Marks 35th Anniversary with Breathtaking New Views
- 2. A Frosty Portrait of Mars
- 3. Rosette Nebula’s Stellar Nursery
- 4. Gorgeous Spiral Galaxy with Patchy Starbirth Swirls
- 5. FAQ About the Hubble Space Telescope
- 6. How has Hubble’s ability to observe beyond Earth’s atmosphere revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos?
- 7. Hubble’s Universe: An Interview with Dr.Aris Thorne
- 8. Hubble’s Legacy of Revelation
- 9. The Technical and Past Importance
- 10. The Human Element
By [Your Name/Agency Name]
As scientists and space enthusiasts celebrate the Hubble Space Telescope’s 35th year orbiting Earth, NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA) have released a collection of awe-inspiring images. These new snapshots showcase the telescope’s continued ability to capture the universe with unparalleled clarity, furthering our understanding of cosmic phenomena.
Launched aboard the space shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990, the Hubble space Telescope was designed to observe “the universe” with clarity and detail, orbiting above Earth’s atmosphere, allowing it to eye celestial wonders “10 times better than the ground-based telescopes of the time.” This clarity has been instrumental in numerous astronomical discoveries and has reshaped our understanding of the cosmos.
Over the past three and a half decades, the observatory has made nearly 1.7 million observations, resulting in more than 22,000 scientific papers. It has amassed over 400 terabytes of archived data and continues to be highly sought after by astronomers, with observing time oversubscribed by a factor of six. This high demand underscores Hubble’s enduring scientific value and its unique capabilities.
“Hubble’s legacy is the bridge between our past and future knowledge of a universe that is unbelievably glorious, as well as rambunctious,” officials with the european Space Agency (ESA), which operates Hubble jointly with NASA, said in a recent statement. “Before Hubble, no generation ever had access to unimaginably vibrant views of space, stretching almost all the way back to almost the beginning of time.”
The newly released snapshots cover a variety of wonders, including seasonal changes on Mars and stars sculpting their environment into celestial art. According to the statement, they were chosen to commemorate the 35th anniversary.
A Frosty Portrait of Mars
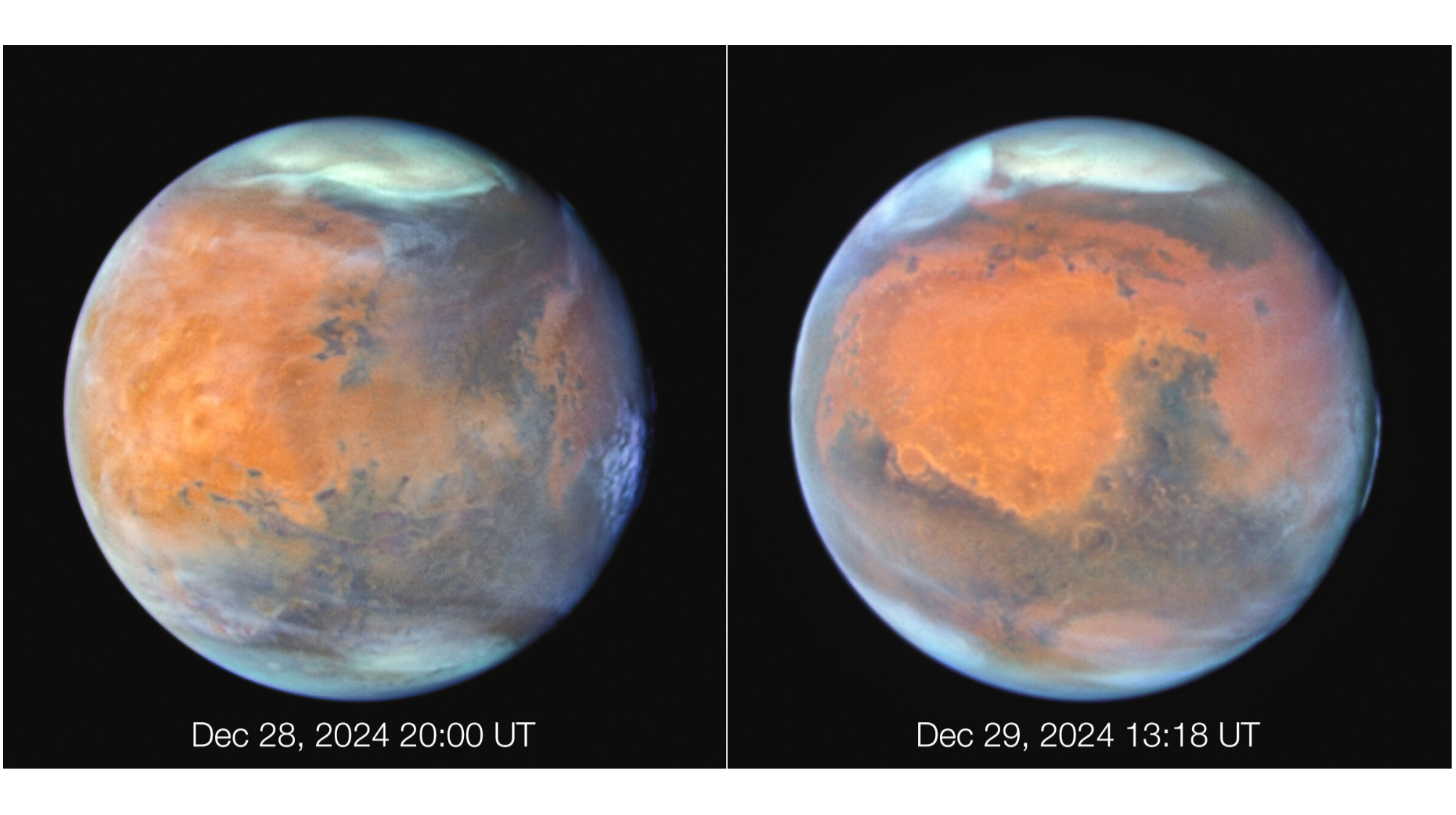
Hubble’s observations of Mars reveal a “frosty Red planet,” its atmosphere veiled by thin water-ice clouds that stand out in ultraviolet light. These images provide valuable data for understanding Martian weather patterns and atmospheric composition.
Recent studies using Hubble data have focused on the seasonal variations in Mars’ atmosphere, particularly the formation and dissipation of these water-ice clouds. Such studies help constrain models used for planning future Mars missions, including those aimed at searching for evidence of past or present life.
Rosette Nebula‘s Stellar Nursery
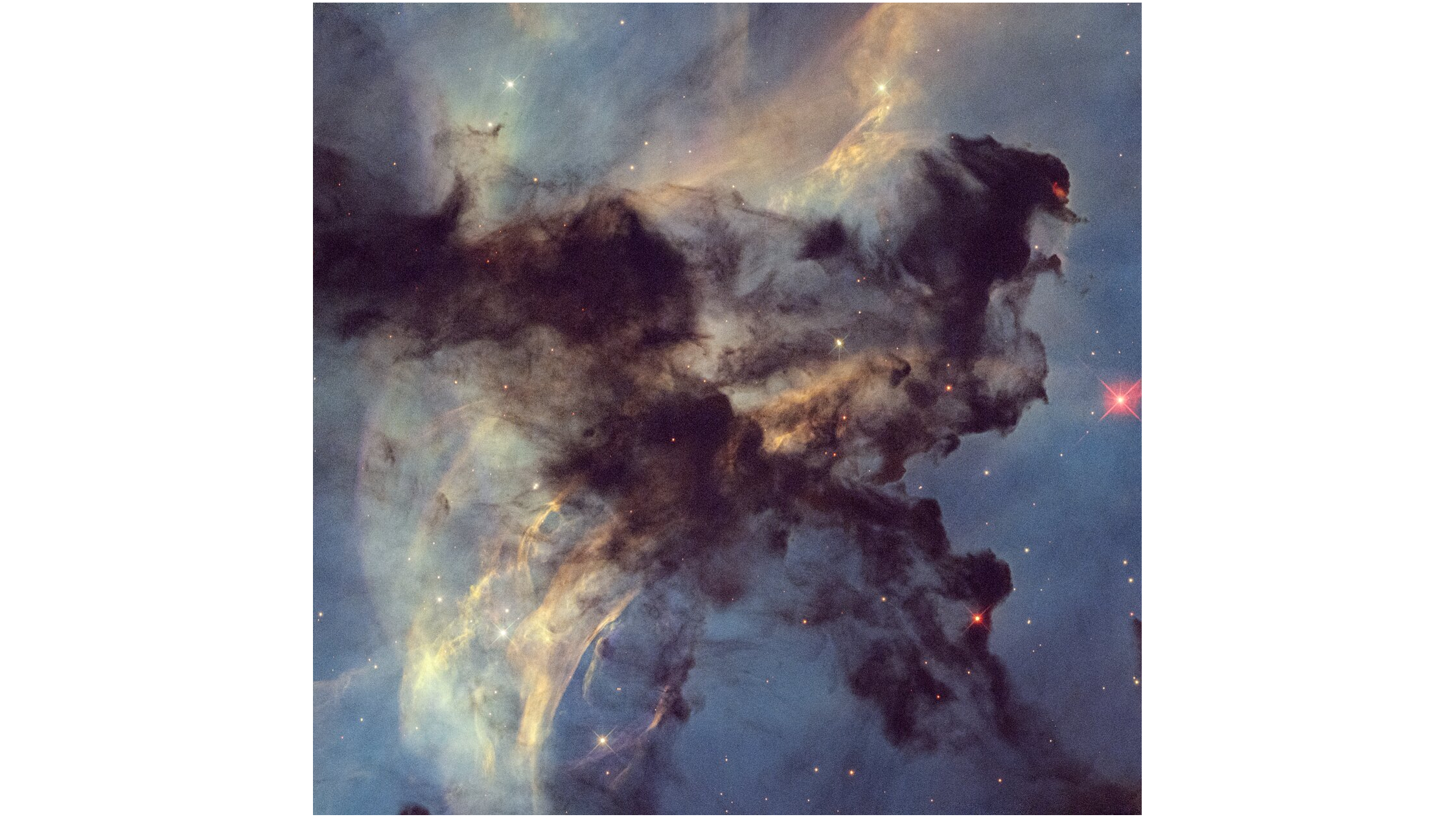

this image provides a breathtaking close-up of a small but dynamic region within the Rosette nebula, a stellar nursery roughly 5,200 light-years from Earth. Silhouetted against the nebula’s luminous backdrop are “stark dark clouds made of hydrogen gas interwoven with dust.”
These dense clouds are not static but are actively being sculpted and eroded by the intense radiation blasted from the energetic cluster of large stars residing at the nebula’s heart, known to astronomers as NGC 2244. The nebula spans 100 light-years, but this view covers just four light-years, according to the statement.
American universities and research institutions frequently utilize Hubble data to study star formation within nebulae like the Rosette. These studies contribute to our understanding of the conditions necessary for stars to be born and the impact of young, massive stars on their surrounding environment.
Gorgeous Spiral Galaxy with Patchy Starbirth Swirls
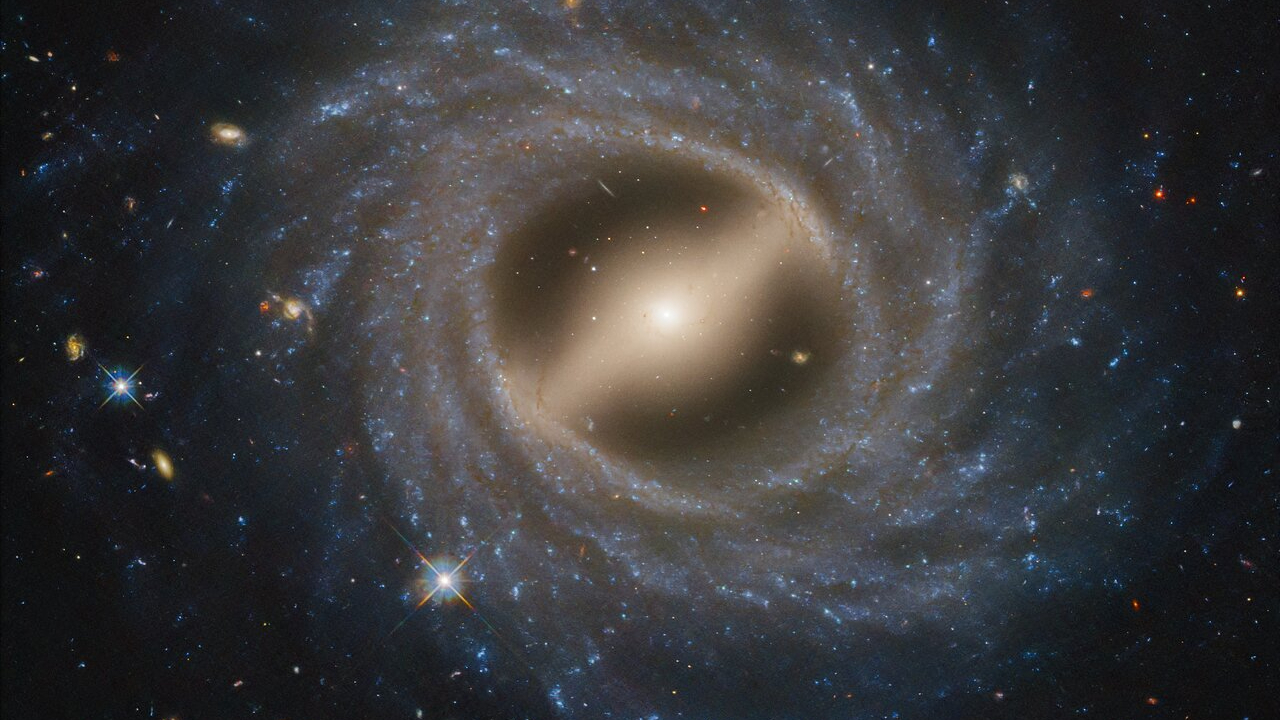

This stunning face-on image showcases the barred spiral galaxy NGC 5335 swirling about 225 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. This galaxy exhibits what astronomers call a “flocculent” structure, with patchy bursts of star formation scattered across its disk, according to the statement.
Unlike many spiral galaxies, including our own Milky Way, NGC 5335 doesn’t feature well-defined arms. The fainter structures that do exist in NGC 5335 spiral counterclockwise as they extend outward from the galactic center.A prominent bar of stars and gas cuts across the galaxy’s bright center, funneling material inward to fuel the birth of new stars. “These galactic bars are temporary features that form and dissolve over billions of years, and are found in about 30% of galaxies, according to the statement.”
American astrophysicists actively study barred spiral galaxies like NGC 5335 to understand the role of galactic bars in galaxy evolution. These structures are believed to play a crucial role in channeling gas and dust towards the central regions of galaxies, influencing the formation of supermassive black holes and the overall star formation rate.
While Hubble has been revolutionary, it is worth noting that some argue that the focus on stunning imagery overshadows the less visually appealing but equally important scientific data it provides. However, the visually stunning images often serve as a powerful outreach tool, inspiring public interest in science and astronomy, which, in turn, supports continued funding for space exploration and research.
FAQ About the Hubble Space Telescope
| Question | answer |
|---|---|
| What is the primary mission of the Hubble space Telescope? | The primary mission is to observe the universe with high resolution,free from the distorting effects of Earth’s atmosphere,enabling detailed studies of celestial objects. |
| How high above Earth does Hubble orbit? | Hubble orbits approximately 340 miles (547 kilometers) above Earth. |
| How many scientific papers has Hubble contributed to? | Hubble observations have contributed to over 22,000 scientific papers. |
| Who operates the Hubble Space Telescope? | Hubble is jointly operated by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). |
| When was the Hubble Space Telescope launched? | Hubble was launched on April 24, 1990. |
How has Hubble’s ability to observe beyond Earth’s atmosphere revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos?
Hubble’s Universe: An Interview with Dr.Aris Thorne
Interviewer: Welcome, Dr. Thorne, and thank you for joining us. Its a pleasure to have you here at Archyde as we celebrate the Hubble Space Telescope’s 35th anniversary. Could you tell us a little about your role?
Dr. Thorne: Thank you for having me! I am a Senior Astrophysicist at the International Astronomical Union,I’ve been following the Hubble Space Telescope’s work for many years.
Hubble’s Legacy of Revelation
Interviewer: Let’s start with a big picture. What, in your opinion, is Hubble’s most significant contribution to our understanding of the universe?
Dr. Thorne: Without a doubt, Hubble’s ability to observe with astonishing clarity, free from the Earth’s atmospheric distortion, has revolutionized our understanding of the cosmos. Its observations have touched every aspect of astronomy,from planetary science to cosmology. It has reshaped our understanding of the cosmos significantly.
Interviewer: the recently released images are stunning. Mars, The Rosette Nebula, a spiral galaxy.Can you elaborate on the scientific value of these new images, particularly in the context of Hubble’s enduring mission?
Dr. Thorne: Absolutely.The images of Mars give us data on its seasonal changes, the water-ice clouds allow us to understand it’s atmosphere. The Rosette Nebula offers new perspectives on star formation. Looking at the galaxy, NGC 5335, allows us to understand galaxy evolution, as these are frequently studied by American astrophysicists. Hubble continues to be a vital tool for astronomers.
The Technical and Past Importance
Interviewer: For our readers, can you briefly explain how Hubble’s orbit, 340 miles from Earth, actually helps it see the universe so clearly?
Dr. thorne: Hubble’s orbit puts it above the Earth’s atmosphere, which distorts light. From this vantage point, it can see with incredible clarity, ten times better than the ground-based telescopes of the time.
Interviewer: The telescope has been up there for over three decades, collecting an enormous amount of data. Can you share some statistics that highlight its extensive scientific impact – the number of observations, scientific papers, and data archived?
Dr. Thorne: Hubble has made nearly 1.7 million observations, which have contributed to over 22,000 scientific papers. It amassed over 400 terabytes of archived data. This demand underlines Hubble’s enduring scientific value.
The Human Element
Interviewer: The images Hubble provides are genuinely awe-inspiring. They spark curiosity and fuel public interest in space exploration. however, some argue the focus on these images overshadows the scientific data. What are your thoughts on that?
Dr. Thorne: While that perspective has some merit, the visual splendor of Hubble’s photos is also crucial. These images do indeed serve as a powerful outreach and communications tool. Their beauty helps inspire interest in science, which is a great tool for funding space exploration.
Interviewer: With so much details and so many groundbreaking discoveries, what do you think is the next big scientific breakthrough we can foresee due to Hubble’s continuous observations?
Dr. Thorne: I am particularly excited about the continued study of exoplanets,those outside our solar system. Hubble’s data is helpful in understanding their atmospheres and potentials for life.I think we’ll probably find some of the answers soon.
Interviewer: One can only dream about it.Dr. Thorne,what do you believe will be Hubble’s ultimate legacy?
Dr. Thorne: Hubble’s legacy isn’t just about what it has seen; it’s about what it enabled. It has inspired generations, helped lay the foundation of our understanding of the universe, and set the stage for future generations of space telescopes. Hubble is truly the bridge between knowing the past and knowing the future.
Interviewer: Dr. Thorne, thank you once again for your time, your insightful comments, and for helping us appreciate the splendid Hubble Space Telescope.It was a pleasure having you.




:format(webp)/nginx/o/2025/04/26/16800069t1hb3da.jpg)

