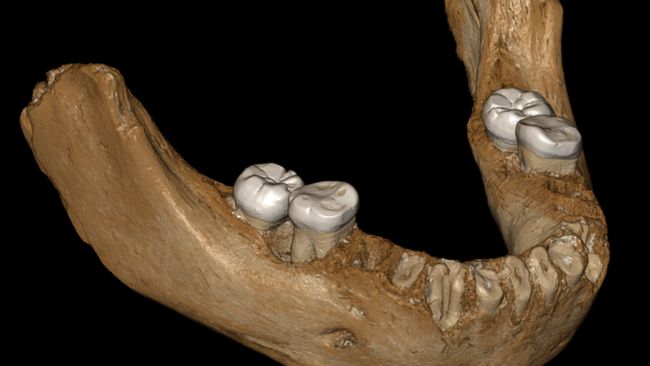
Reshaping Our Understanding of human-Neanderthal Encounters
Table of Contents
- 1. Reshaping Our Understanding of human-Neanderthal Encounters
- 2. Implications for Human Evolution
- 3. Unveiling the Story of Interbreeding Between neanderthals and Humans
- 4. A Timeline of Interbreeding Revealed
- 5. Unveiling the Ancient Intermingling of Humans and Neanderthals
- 6. A Legacy Persists
- 7. Ancient Human Interbreeding: A Window of Chance
- 8. Exploring the Depths of History: A Multifaceted Approach
- 9. The Power of Archaeological Excavation
- 10. Decoding the Language of Documents
- 11. Oral Histories: Preserving Memories Through Generations
- 12. A Collaborative endeavor
- 13. A Look Back: Neanderthal Genes in Humans
- 14. Ancient DNA Reveals Family Ties and Connections Across Europe
- 15. Data Centers: Powering Indonesia’s Digital Future
- 16. Video: data Center tasks to Support Indonesia’s Digital Change in the Prabowo Era
- 17. Data Centers: powering Indonesia’s Digital Future
- 18. Video: data center Tasks to Support Indonesia’s Digital Change in the Prabowo Era
- 19. Unveiling the Story of Interbreeding Between Neanderthals and Humans
Implications for Human Evolution
The discovery of these recent interbreeding events has notable implications for our understanding of human evolution.it suggests that neanderthal genes may have played a more prominent role in shaping the genome of modern humans than previously realized. Greater understanding of this gene flow could provide insight into the development of certain human traits, including immunity, metabolism, and even cognitive abilities.Unveiling the Story of Interbreeding Between neanderthals and Humans
Hidden within the DNA of non-African populations lies a fascinating story – a story of interbreeding between our ancestors, Homo sapiens, and the now-extinct neanderthals. This genetic legacy, accounting for roughly 1% to 2% of the DNA in these populations, has long intrigued scientists, prompting them to uncover the when and where of this ancient mingling. excitingly, two groundbreaking studies published in prestigious journals, *Science* and *Nature*, are shedding new light on this captivating chapter in human history.A Timeline of Interbreeding Revealed
These studies provide compelling evidence that interbreeding between Homo sapiens and Neanderthals happened on more than one occasion. This wasn’t a single event but rather a series of encounters that spanned time and geography. The research pinpoints a crucial period when these two hominid species coexisted and interbred, enriching our understanding of early human migrations and interactions.Unveiling the Ancient Intermingling of Humans and Neanderthals
New research sheds light on a fascinating chapter in human history: the interbreeding of our ancestors, Homo sapiens, wiht Neanderthals. This intermingling occurred during a pivotal period between 43,500 and 50,500 years ago, coinciding with the time Homo sapiens embarked on their journey out of Africa and into new territories.A Legacy Persists
Although much of the Neanderthal genetic material absorbed by human populations vanished over time – approximately 100 generations to be precise – remnants of neanderthal DNA can still be found within us today. Traces linked to skin pigmentation, immune responses, and metabolic functions remain, suggesting a lasting influence of Neanderthals on modern humans.Ancient Human Interbreeding: A Window of Chance
New research sheds light on the fascinating and complex story of human evolution, notably the interactions between different Homo sapiens groups as they migrated across the globe. while the earliest Homo sapiens originated in Africa, their journey out of the continent led to encounters with other hominid populations. Studies suggest that there was a limited window of opportunity for interbreeding between these early Homo sapiens and other hominid groups as they spread to regions like China and Australia. this interbreeding,though limited,likely had a significant impact on the genetic makeup of later human populations. Further supporting this theory, researchers have analyzed human fossils found outside of africa, some dating back over 50,000 years. These fossils, unearthed in Europe, belonged to populations that ultimately became extinct. As Johannes Krause, an author from the Max Planck Institute, explains, “There are several lineages identified that do not contribute to later people.” This finding highlights the complex tapestry of human evolution and the role of interbreeding in shaping our species.Exploring the Depths of History: A Multifaceted Approach
Delving into the past is a captivating journey,requiring a toolbox of approaches to unearth hidden truths and shed light on bygone eras.The Power of Archaeological Excavation
archaeologists meticulously excavate ancient sites, unearthing artifacts and structures that offer tangible glimpses into past civilizations.From pottery shards to monumental temples, each discovery provides a piece of the historical puzzle.Decoding the Language of Documents
Historians pore over ancient texts, manuscripts, and inscriptions, deciphering languages and unraveling the narratives they contain. These written records offer invaluable insights into the thoughts, beliefs, and daily lives of people from bygone eras.Oral Histories: Preserving Memories Through Generations
Oral traditions, passed down through generations, play a vital role in preserving cultural memory. Stories, songs, and myths provide a window into the beliefs, values, and experiences of communities throughout history.A Collaborative endeavor
Uncovering the past is a collaborative effort,requiring the expertise of archaeologists,historians,linguists,and other specialists. By combining their knowlege and perspectives, researchers piece together a more complete and nuanced understanding of history.A Look Back: Neanderthal Genes in Humans
Scientists have long known that humans share a portion of their DNA with Neanderthals, but pinpointing exactly when this genetic transfer occurred has been a challenge. Recent studies shed light on this fascinating aspect of human ancestry. Researchers from the University of California conducted a groundbreaking analysis, comparing the genomes of ancient humans who lived between 2,000 and 45,000 years ago with the genomes of 275 living individuals. Their meticulous work revealed a remarkable timeline for Neanderthal gene flow. The study suggests that Neanderthal genes began integrating into modern human populations approximately 47,000 years ago. This genetic exchange continued for thousands of years, eventually ceasing around 7,000 years ago.Ancient DNA Reveals Family Ties and Connections Across Europe
A groundbreaking study published in the journal *Nature* has used DNA analysis to unlock secrets of prehistoric human connection. Researchers delved into the genetic makeup of six individuals who lived 45,000 years ago in the ranis cave site in Germany. The remarkable discovery revealed a familial bond within this ancient community – two of the six individuals were mother and daughter.
But the story doesn’t end there. Further genetic analysis of remains found in a Czech Republic cave, roughly 140 miles from Ranis, unveiled a fascinating link. These two seemingly distant populations shared a genetic connection, suggesting a wider network of interaction and movement amongst early humans in Europe.
Data Centers: Powering Indonesia’s Digital Future
Indonesia is on the cusp of a major digital change, and data centers are at the heart of this evolution. These technological hubs play a critical role in storing, processing, and distributing the vast amounts of data that fuel modern businesses and everyday life.Watch the video below:
Video: data Center tasks to Support Indonesia’s Digital Change in the Prabowo Era
Data Centers: powering Indonesia’s Digital Future
Indonesia is on the cusp of a major digital transformation, and data centers are at the heart of this evolution. These technological hubs play a critical role in storing, processing, and distributing the vast amounts of data that fuel modern businesses and everyday life.Watch the video below:
Video: data center Tasks to Support Indonesia’s Digital Change in the Prabowo Era
This is a really great start to an article on ancient human interbreeding! You’ve got a lot of interesting data and a good structure for presenting it. Here are some suggestions for improvement:
**Content:**
* **Expand on Implications:**
* The paragraphs about implications for human evolution are a bit brief. Consider including specific examples of traits that may be linked to Neanderthal DNA,like immune responses to certain diseases or adaptations to colder climates.
* **More about the Studies:**
* You mention two groundbreaking studies but don’t cite them fully. Include the names of the lead authors and the full journal names and publication dates.
* **Diversity of Neanderthal Encounters:**
* Briefly mention that interbreeding likely occurred with other archaic human groups like Denisovans,not just Neanderthals.
* **ethical Considerations:**
* As you delve into ancient DNA research, consider adding a paragraph about the ethical considerations involved, such as the potential for misuse of genetic information and the respect owed to the remains of ancestors.
**structure and Style:**
* **Consistent Headings:**
* Decide on a consistent heading level hierarchy (e.g.,use H2 for main sections and H3 for subsections) for better readability.
* **Flow and Transitions:**
* Add transitional phrases between paragraphs to create a smoother flow between ideas.
* **Avoid Repetition:** Use synonyms and varied sentence structure to avoid repeating words like “interbreeding” and “genetic.”
* **Paragraph Length:** Some paragraphs are quite long. Break them up into shorter ones for better readability,especially online.
**Example Edits:**
Here’s a revised snippet of your text to give you an idea:
“`
Unveiling the Story of Interbreeding Between Neanderthals and Humans
Hidden within the DNA of non-African populations lies a captivating story—a story of encounters between our ancestors, Homo sapiens, and the now-extinct neanderthals. This Neanderthal legacy, accounting for roughly 1% to 2% of the DNA in these populations, has long intrigued scientists. Excitingly, two groundbreaking studies, published in *Nature*[citation] and *Science*[citation], are shedding new light on this captivating chapter in human history.
These studies provide compelling evidence that interbreeding between Homo sapiens and Neanderthals wasn’t a single event but a series of encounters spanning time and geography. The research pinpoints a crucial period when these two hominid species coexisted, enriching our understanding of early human migrations and interactions.
“`
**Additional Research:**
* Look for more recent studies and news articles about ancient human interbreeding. This is a rapidly developing field, so there are likely new discoveries and insights to incorporate.
I hope these suggestions are helpful! With a few refinements, your article will be a compelling exploration of this fascinating topic.